
引言
你已经了解逻辑综合的过程
- 解析 -> 细化 -> 粗粒度综合 -> 细粒度综合 -> 工艺映射 -> 网表生成
本次课内容:
- 用开源EDA工具评估综合后的电路
- 什么样的Verilog代码会综合出什么样的电路逻辑
- Verilog的RTL综合语义
用开源EDA工具评估综合后的电路
电路的评估
网表中的标准单元是可制造的, 具备各种物理属性
- 可以对电路的好坏进行初步评估
- 衡量电路的三个常用维度: 性能, 功耗, 面积
- 统称为PPA(Performance, Power, Area)
面积评估:
.lib文件已经给出了标准单元的面积属性- 综合器只需要统计每个标准单元的实例化次数, 即可计算出总面积
性能评估: 主要通过频率来衡量, 即电路每秒最多能工作多少次
- 又取决于: 完成一次工作最少需要花多少时间
- 一次工作 = 时序逻辑元件在时钟信号的驱动下更新状态
- 这些指标和时间相关, 分析它们的过程称为时序分析(timing analysis)
性能评估

回顾数字电路的状态机模型:
- 时序逻辑元件在时钟信号到来时更新状态
- 新状态由组合逻辑计算得到, 但需要经过一定的延迟
- 需要控制时钟频率,
使两次时钟之间的间隔(也即周期)能足够容纳组合逻辑的延迟
- 否则, 用于更新状态的数据信号并不是由组合逻辑计算出的稳定结果
评估电路的性能 = 通过评估电路中组合逻辑的延迟, 来推算电路的最高工作频率
- 如果电路的实际工作频率更高,
电路中某些时序逻辑元件的新状态将不符合设计预期
- 从而无法让电路按照预期开展工作
- 例子: 电子发烧友玩超频, 导致电脑卡死
关键路径
电路中的组合逻辑有很多
电路的工作频率受限于电路中延迟最长的一条组合逻辑路径
- 称为电路的
关键路径(critical path)
寻找电路中的关键路径:
- EDA工具从标准单元库中读出标准单元的延迟信息
- 根据网表的拓扑结构, 计算出组合逻辑路径上所有标准单元的总延迟
- 总延迟最长的路径即为电路的关键路径
上述方法基于网表和标准单元库的延迟信息, 不涉及电路的工作过程
- 称为静态时序分析(STA, Static Timing Analysis)
yosys-sta项目中采用iSTA工具来开展STA工作- ICsprout55这个PDK的标准单元库中已经包含完整的延迟信息
两种延迟
当前得到的时序报告并不能完全反映芯片流片时的频率
- 网表只包含标准单元及其拓扑信息, 但未包含标准单元的物理位置信息
- 准确的延迟信息 = 逻辑延迟(logic delay) + 线延迟(net delay)
- 逻辑延迟 = 信号经过标准单元本身的延迟, 由标准单元库给出
- 线延迟 = 信号在两个标准单元之间的线网进行传播的延迟
- 需要开展布局和布线工作后才能得到
虽然逻辑延迟虽然不能代表最终的延迟信息, 但也给出了频率的上限
- 已经能反映出RTL逻辑设计阶段的某些问题(如逻辑过于复杂)
- 足够帮助RTL设计者对RTL设计进行初步评估, 从而进行快速迭代优化
- 对于复杂的高性能处理器, 需要数天时间才能完成一轮物理设计工作
处理器的另一个性能指标
对于处理器来说, 频率并不是衡量其性能的唯一因素
- 频率的另一种理解是每秒工作了多少个周期
- 但不一定每个周期都有
实质性的工作
处理器的本分工作是执行程序
- 处理器的性能应该解读为
执行程序的效率 - 更具体地, 处理器执行的是程序中的指令
- 如果处理器的频率很高, 但要过很久才执行一条指令, 整体上也算不上一个好的处理器
- 衡量处理器执行指令效率的指标 - IPC(Instruction Per Cycle)
- 衡量处理器每周期执行的平均指令数
我们将在B阶段进一步讨论IPC的测量和优化方法
功耗评估
功耗分三类:
- 内部功耗(Internal Power)
- 晶体管翻转时, nMOS和pMOS并非瞬间就完成状态切换
- 在一段很短的时间内, nMOS和pMOS会同时处于导通状态
- 电源端到地端短路, 所产生的功耗就是内部功耗
- 也称短路功耗, 属于动态功耗(dynamic power)的一部分
- 翻转功耗(Switch Power)
- CMOS电路翻转时, 要对相应等效电容进行充/放电
- 这个过程产生的功耗就是翻转功耗
- 也称开关功耗, 属于动态功耗的一部分

动态功耗 = 内部功耗 + 翻转功耗
功耗评估(2)
- 漏电功耗(Leakage Power)
- 在理想情况下, 晶体管处于截止状态时, 源极和漏极之间没有任何电流通过
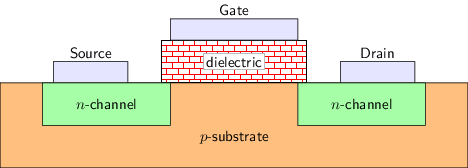
- 真正的晶体管会因为多种原因, 导致在源极和漏极之间存在一定的微小电流, 称为漏电电流(leakage current)
- 由漏电电流形成的功耗就是漏电功耗
- 由于漏电功耗在晶体管不翻转时也会存在, 因此也称为静态功耗
yosys-sta评估电路中所有标准单元的功耗之和
- EDA工具需要从标准单元库中读出标准单元的功耗信息
- 计算出每个标准单元的功耗, 从而计算出总功耗
- 翻转功耗为
0: 等效电容还和走线的拓扑和长度相关
- 翻转功耗为
开放讨论: 还需要FPGA吗?
基本上不需要了
- 从准确度来说, yosys的综合流程是面向ASIC设计的
- 其原理和报告的准确度都更适合一生一芯
- FPGA流程的原理与ASIC不同, 无法替代ASIC流程
- 即使FPGA流程正确, 规范的ASIC流程仍然需要进行网表仿真
- 从时间来说, FPGA的主要作用是仿真加速
- 如果仿真任务并不需要花费很长时间, 使用FPGA的优势并不明显
- 从调试难度来说, FPGA的调试手段很有限
- 只能在时间和空间均受限的条件下抓取底层的波形信息
- 软件仿真则灵活很多, 还可以借助很多软件方法来提升调试的效率
开放讨论: 还需要FPGA吗? (2)
事实上, 当以下不等式成立时, FPGA在时间方面的优势才能体现出来:
\[T_{FPGA.syn} + T_{FPGA.impl} + T_{FPGA.run} < T_{Sim.comp} + T_{Sim.run}\]
- 其中, \(T_{FPGA.syn} + T_{FPGA.impl}\)通常达到小时量级
- 而\(T_{Sim.comp}\)通常能在数分钟内完成
- 因此, 只有当\(T_{Sim.run}\)达到小时量级,
上述不等式才有可能成立
- 不过你很难遇到需要小时量级的时间才能完成的仿真任务
- 而当你遇到这样的任务时, 我们也会对FPGA的评估过程提出更高要求
- 在B阶段中继续讨论这个问题
Verilog的RTL综合语义
Verilog RTL综合标准规范
什么样的RTL代码转换成什么样的标准单元, 需要考虑RTL综合的语义
- 但Verilog标准手册定义的是仿真语义, 不适用于RTL综合这一场景
- Verilog
RTL综合标准手册专门描述了Verilog语言在综合场景下的语义
- 综合器读入Verilog代码, 然后根据这一标准手册所描述的语义, 将Verilog代码转换成语义等价的标准单元
手册的1.1节介绍了RTL综合的一些概述
1.1 Scope
This standard defines a set of modeling rules for writing Verilog® HDL descriptions
for synthesis. Adherence to these rules guarantees the interoperability of Verilog
HDL descriptions between register-transfer level synthesis tools that comply to this
standard. The standard defines how the semantics of Verilog HDL are used, for
example, to describe level- and edge-sensitive logic. It also describes the syntax
of the language with reference to what shall be supported and what shall not be
supported for interoperability.Verilog RTL综合标准规范(2)
1.1 Scope
This standard defines a set of modeling rules for writing Verilog® HDL descriptions
for synthesis. Adherence to these rules guarantees the interoperability of Verilog
HDL descriptions between register-transfer level synthesis tools that comply to this
standard. The standard defines how the semantics of Verilog HDL are used, for
example, to describe level- and edge-sensitive logic. It also describes the syntax
of the language with reference to what shall be supported and what shall not be
supported for interoperability.- 这份标准规范定义了一个建模规则的集合, 来将Verilog用于综合
- 遵循这些规则, 可以保证Verilog代码在符合这份标准的不同RTL综合工具之间得到相同的解释
- 这份标准定义了如何使用Verilog的语义, 例如, 用来描述电平敏感和边沿敏感的逻辑
- 此外, 还描述了Verilog语法中, 哪些是综合器需要支持的,
哪些是综合器不支持的
- 这说明, 综合器支持的Verilog语法, 只是Verilog整体语法的一个子集
Verilog RTL综合标准规范(2)
Use of this standard will enhance the portability of Verilog-HDL-based designs
across synthesis tools conforming to this standard. In addition, it will minimize
the potential for functional mismatch that may occur between the RTL model and the
synthesized netlist.- 采用这份标准可以提升Verilog设计在不同综合器之间的可移植性
- 从而让符合标准的综合器能按一致的语义来解析符合标准的Verilog代码
- 采用这份标准也可以尽可能避免RTL模型和综合网表之间功能不一致的潜在风险
我们关注的内容:
- Verilog的RTL综合语义
- 什么样的Verilog代码会引起仿真行为和综合行为的不一致
对组合逻辑进行建模
第5.1节介绍了对组合逻辑建模的方式
Combinational logic shall be modeled using a continuous assignment or a net
declaration assignment or an always statement.组合逻辑可以通过连续赋值,
线网声明赋值或always语句进行建模
采用连续赋值和线网声明赋值方式时, 所描述的组合逻辑电路和运算符有关
- 手册未介绍运算符与组合逻辑电路的对应关系
- 可以根据Verilog的仿真行为进行推导
从运算符到电路
- 算术运算符
+和-运算符将综合出加法器*将综合出阵列乘法器/和%将综合出阵列除法器- 阵列乘法器和阵列除法器的电路延迟较大
- 在面向高性能的处理器设计中,一般会编写其他类型的乘法器和除法器来提升处理器的主频
- 位运算符
~运算符将综合出数量与位宽相同的非门- 若信号
a的位宽为4,则~a将会综合出4个非门
- 若信号
&,|,^和^~(或~^)将综合出数量与位宽相同的2输入门电路, 分别对应与门, 或门, 异或门和同或门
从运算符到电路(2)
- 归约运算符
&,|和^将分别综合出一个输入端口数量与操作数位宽相同的门电路, 分别对应与门, 或门和异或门- 若信号
a的位宽为4,则&a将会综合出一个4输入的与门
- 若信号
~&,~|和~^各自综合出的电路, 分别等价于在&,|和^综合出的与门, 或门和异或门之后再添加一个非门
- 逻辑运算符
- 将操作数转换为布尔值:
|a为1’b1, 当且仅当a的真值不为零 - 逻辑运算符的行为可以通过归约运算符和位运算符表达
a && b->(|a) & (|b)a || b->(|a) | (|b)!a->~(|a)
- 将操作数转换为布尔值:
从运算符到电路(3)
- 等式运算符
- 等式运算符的行为可以通过归约运算符和位运算符表达
(a == b)->~(|(a ^ b))(a != b)->|(a ^ b)
- 等式运算符的行为可以通过归约运算符和位运算符表达
- 关系运算符
- 用加法器做减法, 根据结果的符号位判断关系的真假
- 位拼接运算符
- 将多个信号按照顺序排列, 组成一个新的向量信号
- 不会综合出额外的门电路
从运算符到电路(4)
- 移位运算符
- 若移位位数为常量,则移位运算符的行为可通过位拼接运算符和下标选择来表达
- 假设被移位操作数
a的位宽为wa,移位位数为b,wa和b皆为常量(a >> b)->{{b{1’b0}}, a[wa-1:b]}(a << b)->{a, {b{1’b0}}}
- 若移位位数为变量,移位运算符将综合出桶形移位器
- 条件运算符
- 将综合出二输入选择器
- 输入输出的位宽与表达式的位宽相同
- 条件对应的电路输出将作为选择器的控制信号
- 两个表达式分别作为选择器的输入端
- 将综合出二输入选择器
用always对组合逻辑进行建模
回到手册第5.1节
When using an always statement, the event list shall not contain an edge event
(posedge or negedge). The event list does not affect the synthesized netlist.
However, it may be necessary to include in the event list all the variables read in
the always statement to avoid mismatches between simulation and synthesized logic.- 使用
always语句时, 事件列表不能包含边沿事件(posedge或negedge)
- 事件列表不影响综合生成的网表
- 但有必要将在
always语句中被读取的所有变量包含在事件列表中, 从而避免仿真和综合结果不一致
用always对组合逻辑进行建模(2)
The event list for a combinational logic model shall not contain the reserved words
posedge or negedge. Not all variables that appear in the right hand side of an
assignment are required to appear in the event list. For example, a variable does not
have to appear in the event list of an always statement if it is assigned a value
with a blocking assignment before being used in subsequent expressions within the
same always statement.- 组合逻辑模型的事件列表不能包含关键字
posedge和negedge
- 并非所有出现在赋值号右侧的变量都需要出现在事件列表中
- 例如, 在一个变量被使用之前,
已经被位于同一个
always语句中的阻塞赋值语句进行赋值
- 例如, 在一个变量被使用之前,
已经被位于同一个
RTFM查看示例
对时序逻辑进行建模
第5.2节介绍了对时序逻辑建模的方式
An edge-sensitive storage device shall be modeled for a variable that is assigned a
value in an always statement that has exactly one edge event in the event list. The
edge event specified shall represent the clock edge condition under which the storage
device stores the value.- 一个边沿敏感的存储元件的建模,
是通过在
always语句中对一个变量赋值来进行的, 这个always语句的事件列表只有一个边沿事件
- 这个边沿事件表示存储元件存储信息时的时钟边沿
Nonblocking procedural assignments should be used for variables that model
edge-sensitive storage devices. Nonblocking assignments are recommended to avoid
Verilog simulation race conditions.- 对于用来建模成边沿敏感的存储元件的变量, 应该使用非阻塞的过程赋值
- 使用非阻塞赋值是为了避免Verilog仿真的竞争条件
对时序逻辑进行建模(2)
Blocking procedural assignments may be used for variables that are temporarily
assigned and used within an always statement.对于临时赋值并在同一条always语句中使用的变量,
可以使用阻塞赋值
RTFM查看示例
- 还有异步复位/置位的描述方式
补充: if-else语句的可综合语义
规则1: 对于只更新单个寄存器变量的嵌套if-else语句,
其功能等价于嵌套的条件运算符
always @(posedge clk)
if (cond1) val <= expr1;
else if (cond2) val <= expr2;
// ...
else if (condn) val <= exprn;
else val <= expr_last;上述代码所描述的电路等价于:
条件运算符会综合出选择器
- 上述代码将综合出链式选择器, 选择结果与触发器的D端相连
补充: if-else语句的可综合语义(2)
规则2: 对于只更新单个寄存器变量的多个并列的if语句,
其功能可用嵌套的if-else语句来表示
补充: if-else语句的可综合语义(3)
规则3:
对于更新多个寄存器变量的if-else语句,其功能等价于按照变量将always语句分开编写
- 前提: 不产生数据竞争
补充: case语句的可综合语义
假设expr0, expr1, …,
exprn中均不含x和z
仿真和综合行为不一致的场景
在芯片设计的流程中, 仿真和综合都是必须的步骤
- 由于仿真和综合的语义不完全一致, 对于同一份Verilog代码, 其仿真行为和综合行为可能不一致
- 考虑到物理设计和制造, 故Verilog代码的行为需要以综合为准
手册的附录B(Functional mismatches)描述了一些不一致的场景
- B.1小节提到的就是不确定性的行为
- 综合器可以自由选择将
0或1作为触发器b的输入 - 但不管如何选择, 由于数据竞争的存在, 综合网表的行为都可能与仿真结果不一致
仿真和综合行为不一致的场景(2)
更多的场景
- 使用Pragmas
- 使用
`ifdef - 事件敏感列表不完整
- 赋值语句的顺序错误
- 同时带有异步复位和异步置位的触发器
- 使用函数
- 使用
casex - 使用
casez - 使用
x赋值语句 - 在变量声明时赋值
- 使用时间延迟
手册包含详细的解释和示例, 建议RTFM仔细阅读
总结
理解综合的结果
- 评估电路的三个常用维度(PPA)
- 性能
- 电路的最高工作频率由关键路径的延迟决定
- 总延迟 = 逻辑延迟 + 线延迟
- 处理器的另一个性能指标 - IPC
- 功耗
- 动态功耗 = 内部功耗 + 翻转功耗
- 静态功耗 = 漏电功耗
- 面积
- 性能
- Verilog的RTL综合语义
- 从运算符到电路
- 用
always对组合逻辑和时序逻辑进行建模 - 需要避免仿真和综合行为不一致的场景


